Valued at $724.48 billion in 2021, the global consumer electronics market is growing rapidly and shows no signs of slowing: and one thing that generates in addition to profits is a mind-boggling amount of e-waste.
According to Precedence Research, the market size is expected to surpass $1.13 trillion by 2030. The surging demand for electronic devices is likely in part due to shifts in work culture post-Covid. Companies such as Google have adopted flexible working hours, whereby people work from home or on-the-go, making them more dependable on devices than ever before. Plus, higher demand for luxury products, technological advancements, new features and a desire to have the latest and greatest smartphone give demand in this sector a boost.
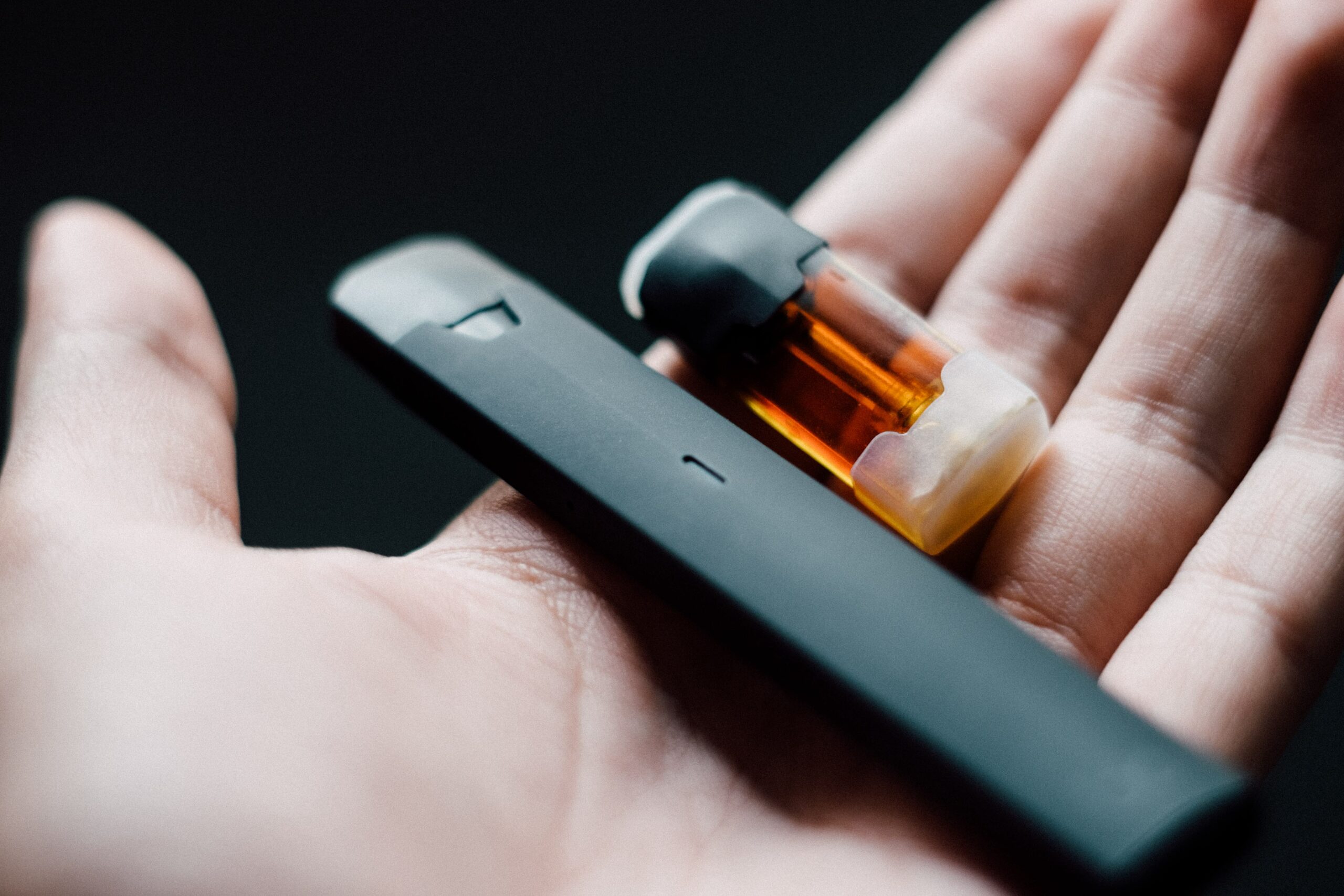
But it’s not just personal productivity gadgets being haphazardly thrown away. As smoking trends evolve, millions of disposable vapes containing valuable metal are ending up in landfills. According to a joint investigation by Sky News and the Bureau of Investigative Journalism, users in the UK are throwing away around two disposable vapes every two seconds. The number of discarded disposable vapes accounts for around 10 tonnes of lithium being sent to landfill or waste incinerators each year — enough of the metal to make batteries for 1,200 electric cars. In the Middle East, the vaping market has grown rapidly due to legalization, high smoking rates and affordability in the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia. E-cigarettes were banned in Qatar in 2012 and then three years later in Oman, but legalized in Bahrain and Kuwait in 2016. Three years later Jordan and the UAE followed suit and legalized vaping, with Saudi Arabia in 2020 adopting international standards for the practice.
As the market continues to grow across the Middle East and the world, so does e-waste. Vape shops are appearing on every retail corner throughout the UAE and with the World Vape Show gearing up for a global tour with stops in Paraguay, London, Dubai and the Philippines, new products are set to enter the market in droves. Consumer behavior is best described as ‘out with the old, in with the new’ but what happens to consumer electronics when consumers decide to level up?
What is e-waste?
Electronic waste or e-waste is defined as any electrical or electronic equipment that’s been discarded. Products include smartphones, tablets, computers, and LED screens that are broken or in good working condition.The challenge of how best to dispose of unwanted electronics isn’t new — it dates back to the 1970 — but a lot has changed since then to keep the toxic chemicals associated discarded electronic devices from harming the environment. Most electronics contain some form of toxic materials, such as beryllium, cadmium, mercury, and lead, which pose serious environmental risks to soil, water, air, and wildlife. When e-waste gets buried in a landfill, it can
deposit microscopic traces of toxic chemicals into the soil. Eventually, leaching occurs whereby these traces of toxic materials pool into the ground below the landfill potentially contaminating groundwater.
According to the Global E-waste Monitor 2020, the generation of e-waste is increasing every year. Globally, e-waste represents 5 percent of the waste generated, but 70 percent of the toxic waste around the globe is from e-waste. In 2019, 53.6 million metric tons (Mt) of e-waste was generated, with that amount projected to hit 74.7 Mt by 2030. Many of the world’s economies are dependent on the huge consumption of electronics and this waste generation is difficult to control with fewer options to repair and recycle waste. Asia is the largest generator of e-waste with 24.9 Mt; the next is America at 13.1 Mt, Europe at 12 Mt, and Africa, which produces 2.9 Mt.
Understanding consumer behavior in the UAE
Studies have shown that demographic and socioeconomic factors play an important role in the recycling behavior of the consumers. The UAE is one of largest consumers of e-devices and consequently, proper disposal is of great importance. E-waste disposal awareness leads to better disposal behaviors. Therefore, a study was commissioned by a consortium of universities in the UAE to understand the e-device purchase and disposal behavior of university communities. As part of the study, a survey was conducted among the students and staff members of the federally funded Zayed University.
The study found that 47.95 percent of respondents purchased mobile phones, and 65 percent of the respondents purchased one to three electronic devices every year. Through the analysis of variance (ANOVA), age and field of specialization were found to affect knowledge about e-waste. Older respondents and those with specialized skills in science were more aware of it, while most of the respondents disposed of e-devices such as batteries, earphones/headphones, and electronic toys along with the household trash. A very small percentage of respondents disposed of e-devices such as laptops, phones, and tablets with the household trash. Mostly, these were either repaired,
donated, or sold to second-hand users. Many respondents were neither aware of the government initiatives on e-waste collection nor participated in government-sponsored e-waste recycling.
The study further identified that 67 percent of the respondents were aware of the toxicity of e-waste, and 61 percent of the respondents were keen to join e-waste recycling drives at the university. The findings of the study imply that the policy makers need to incentivize e-waste-disposal systems and develop targeted awareness approaches to encourage residents and citizens to adopt responsible habits
with respect to e-waste disposal in the UAE.
The solution
The UAE is committed to creating a circular economy, which emphasizes protection of environment and in turn leads to socio-economic benefits. It pushes for reduction in utilization of primary resources and emphasizes waste minimization by closing the loop of products, product parts, and materials. In a circular economy, companies see cost-saving opportunities in strategies such as resource efficiency, resource loop closing, enhanced reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling. With worldwide increase in e-waste, it is imperative that e-waste management is a part of the framework for any global circular economy. A push for technical innovation in this sector will also lead to
financial incentives for poorer regions of the world, as e-waste dumping and dismantling mainly occur there.
The UAE established the Integrated Waste Management system to divert solid waste away from landfills. At the time, the goal was to reduce total municipal solid waste by 75 percent by 2021. Today, local municipalities also support private organizations in their quest to better manage electronic waste throughout the country with proper e-waste recycling. So, if you’re looking for an upgrade or simply planning to part with unused electronics, check out these services:
1. Enviroserve
From humble beginnings doing mobile phone collections and dismantling, Enviroserve has grown to become one of the most trusted electronics recyclers and processors in Dubai. It specializes in electronic waste recycling, IT asset disposition and refurbishment, brand protection (special waste) and refrigerant gas recycling. Enviroserve follows EU standards for recycling e-waste and the company is also endorsed by the Ministry of Environment to destroy, dismantle and repurpose electronic waste. They have also earned impressive accolades including the UAE SME of the Year Award in 2007, Electrical & Electronic Equipment Processor of the Year in 2018 and 2019 and a Dubai Industrial City Environmental and Sustainability Award in 2019.
2. Averda Dubai
Averda Dubai is committed to providing a sustainable waste management system in Dubai. The company works in partnership with Dubai Municipality and also serves commercial customers across a variety of industries. Services include e-waste pick-up, which customers can schedule at their convenience. The company is self-sufficient and uses cutting-edge technology to repurpose electronic waste. Averda uses its own transformers to convert waste into useful materials such as aluminum. Furthermore, their Smart Recycling Centers use sensors and solar panel-powered mechanisms to sift through deposited waste.
3. New Green Star Electronic Recycling Company
New Green Star Electronic Recycling Company is a certified recycler servicing Dubai and Abu Dhabi. The company offers IT asset disposal and buy-back from individuals and corporations to refurbish and resell obsolete equipment, giving outdated electronic devices a new purpose. This movement also helps others secure “new” electronics at affordable prices. New Green Star also understands the need to handle sensitive electronic data with care as they have technicians extract hard drives and storage media to be destroyed. They permanently erase data from all storage and media units before repurposing them. The storage units are disintegrated and shredded to eliminate the risk of theft or misappropriation of recyclable components.
4. Recycling Emirates
Recycle Emirates provides computer and e-waste recycling services, offering a one-stop comprehensive recycling service. Recycle Emirates properly disposes of old or unused electronics, such as monitors, hard drives, computers, printers, phones and so much more with zero impact to landfills and the environment. Expertise in electronic recycling and a commitment to superior customer service makes Recycle Emirates an ideal partner for electronic recycling in Dubai, UAE & GCC.